Project management is a dynamic discipline that plays a pivotal role in the successful execution of endeavours across various industries. With its multifaceted functions, project management acts as the guiding force that transforms ideas into reality. According to Investopedia, Project management entails the planning and organisation of a company's resources in order to complete a certain work, event, or obligation. It can be a one-time project or a continuous effort, with resources such as staff, funds, technology, and intellectual property controlled. In this article, we will delve into the essential functions of project management, exploring how it ensures efficiency, quality, and success in the completion of diverse projects.

Planning and Initiation:
The foundation of any successful project lies in meticulous planning and initiation. Project managers, in collaboration with stakeholders, define the project's scope, objectives, and deliverables. They conduct a comprehensive analysis of the project's feasibility, considering factors such as time, budget, and available resources. This stage sets the groundwork for the entire project life cycle, laying the framework for subsequent functions. Effective planning is the cornerstone of project management. This function involves creating a detailed project plan that outlines tasks, timelines, resource requirements, and risk mitigation strategies. A well-structured plan not only guides the project team but also helps in managing expectations, identifying potential challenges, and allocating resources efficiently.
Resource Allocation and Scheduling:
Effective resource allocation is a core function of project management. Once the project scope is defined, project managers identify and allocate resources such as manpower, finances, and materials. Scheduling comes into play as project managers create timelines, milestones, and deadlines. Tools like Gantt charts are commonly employed to visualise project schedules, aiding in efficient time management.
Risk Management:
No project is without its challenges, and identifying potential risks is a critical function of project management. Project managers conduct risk assessments to anticipate obstacles that may arise during project execution. Mitigation strategies are developed to address these risks, ensuring a proactive approach to challenges rather than a reactive one. By identifying and managing risks early on, project managers enhance the project's resilience and adaptability.
Communication and Collaboration:
Clear and effective communication is the backbone of successful project management. Project managers facilitate communication among team members, stakeholders, and other relevant parties. They ensure that everyone involved is on the same page regarding project goals, progress, and any changes in scope. Collaboration tools and regular status meetings help foster a cohesive team environment, promoting synergy among project participants. Effective communication is a pervasive function throughout the project lifecycle. Project managers must facilitate clear and open communication among team members, stakeholders, and any external parties involved. Regular updates, status reports, and addressing concerns promptly contribute to a cohesive and informed project environment.
Execution and Monitoring:
The execution phase involves putting the project plan into action. Project managers oversee the team's activities, ensuring that tasks are completed according to the established schedule. Monitoring becomes crucial during this stage, with project managers tracking progress, identifying deviations from the plan, and implementing corrective actions as needed. Real-time monitoring tools contribute to informed decision-making, allowing for adjustments to keep the project on track. Execution is where the rubber meets the road. During this phase, project managers coordinate resources, implement the project plan, and monitor progress. Communication and collaboration are key elements as teams work towards achieving milestones and deliverables. Timely problem-solving and adherence to the established plan are crucial for a successful execution phase.
Quality Control:
Maintaining high-quality standards is a non-negotiable aspect of project management. Project managers implement quality control measures to ensure that deliverables meet predefined standards. This involves continuous evaluation of work processes, adherence to best practices, and the use of quality assurance techniques. By prioritising quality, project managers safeguard the project's success and enhance overall stakeholder satisfaction. Constant monitoring and control are essential to ensure that the project stays on course. Project managers use key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess progress, track deviations from the plan, and address issues promptly. This function involves risk management, quality control, and continuous evaluation to maintain project alignment with goals and objectives.
Change Management:
Adaptability is a hallmark of effective project management. Change is inevitable in any project, whether it be alterations to the scope, unexpected challenges, or shifting priorities. Project managers implement change management strategies to assess the impact of changes, communicate these changes to relevant stakeholders, and ensure a smooth transition without compromising project objectives.
Closing and Evaluation:
As the project nears completion, project managers oversee the closing phase. This involves finalising all project deliverables, obtaining stakeholder approvals, and ensuring that project outcomes align with initial objectives. Post-project evaluations are conducted to analyse the overall success of the project, identifying areas for improvement and capturing lessons learned for future endeavours. Closing a project is not just about finishing tasks but also about ensuring that the project's objectives have been met. Project managers oversee the completion of deliverables, obtain client or stakeholder approval, and conduct a comprehensive project review. The closure phase involves documentation, knowledge transfer, and celebrating team achievements.
Conclusion:
In essence, project management is a multifaceted discipline that encompasses planning, resource management, risk mitigation, communication, quality control, adaptability, and evaluation. These functions are interconnected, forming a comprehensive framework that guides projects from conception to completion. Successful project management is not only about achieving specific objectives but also about fostering collaboration, adapting to change, and ensuring that every stakeholder's expectations are met. As industries continue to evolve, the role of project management remains pivotal in navigating the complexities of modern endeavours.
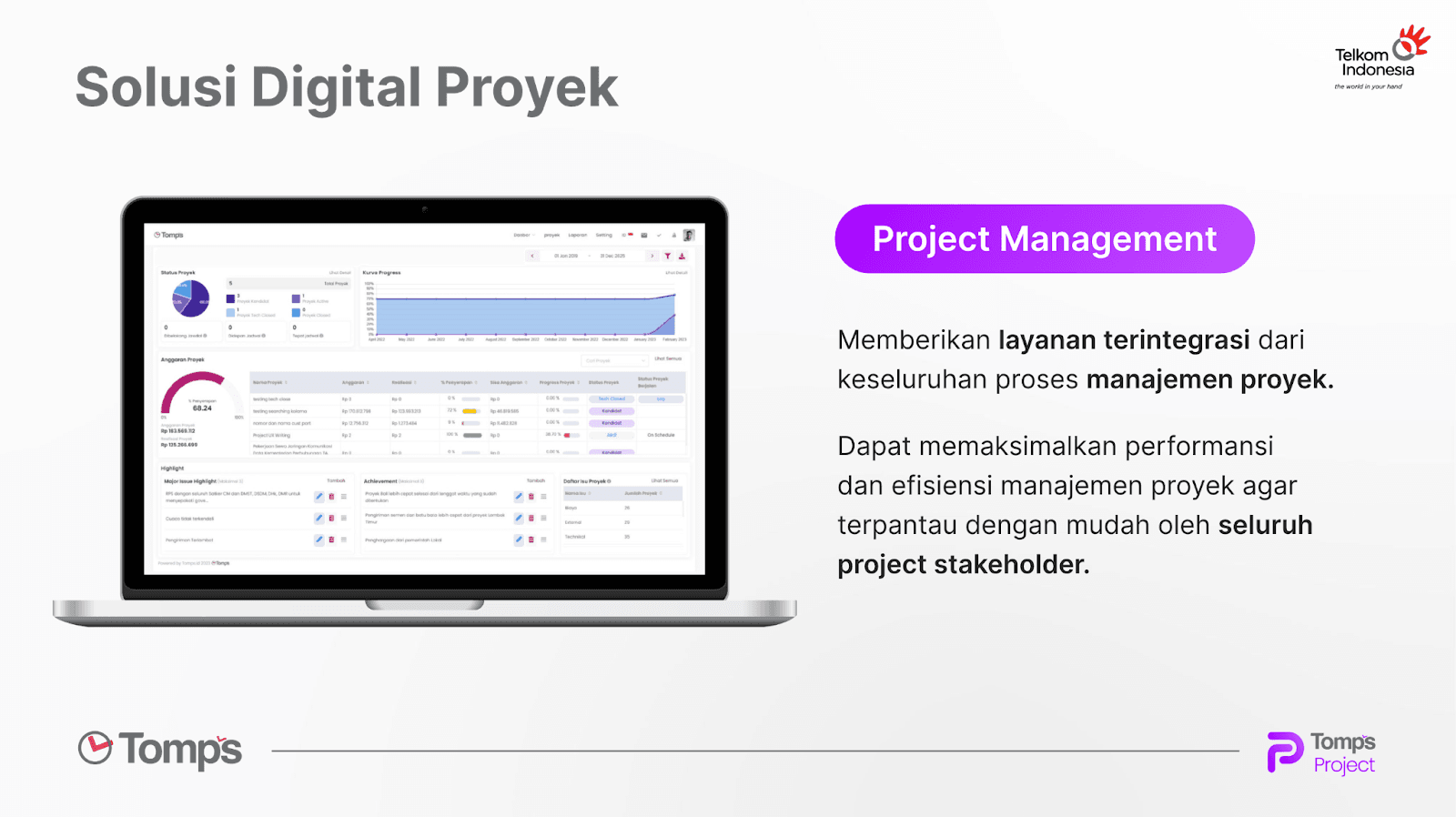 Tomps is an innovative solution that will change the way you manage projects. With advanced features and an intuitive interface, Tomps Project provides complete control over every aspect of your project. Leverage risk management functionality, efficient planning, and real-time reporting to ensure the success of your projects. With Tomps Project, you can increase productivity, reduce risk, and achieve your project goals more effectively. Don't let your projects get stuck, switch to Tomps Project today and watch your projects transform into incredible success!
Tomps is an innovative solution that will change the way you manage projects. With advanced features and an intuitive interface, Tomps Project provides complete control over every aspect of your project. Leverage risk management functionality, efficient planning, and real-time reporting to ensure the success of your projects. With Tomps Project, you can increase productivity, reduce risk, and achieve your project goals more effectively. Don't let your projects get stuck, switch to Tomps Project today and watch your projects transform into incredible success!